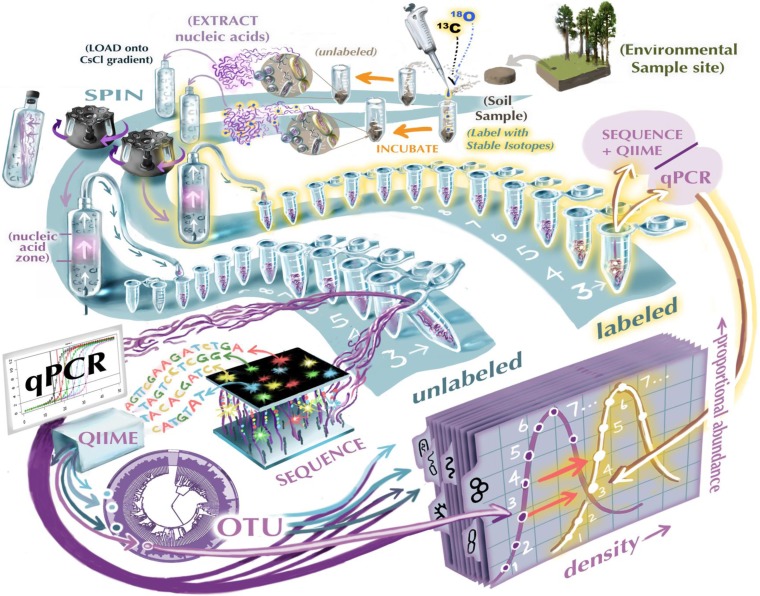
Soil mineral assemblage and substrate quality effects on microbial priming
Native soil organic carbon (SOC) decomposition rates may be altered through increased carbon (C) input, a phenomenon known as SOC priming (Blagodatskaya et al., 2011). Quantifying priming is important because it may modulate long-term SOC storage in ecosystems and therefore C biogeochemical cycling. Priming is positive when more SOC is decomposed or, […]