Decomposition of Senesced leaf litter is faster in tall compared to low birch shrub tundra
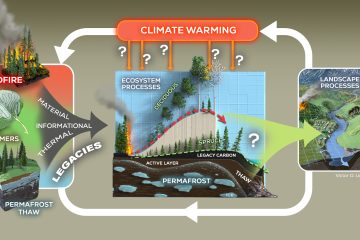
Many Low Arctic tundra regions are currently undergoing a vegetation shift towards increasing growth and groundcover of tall deciduous shrubs due to recent climate warming. Vegetation change directly affects ecosystem carbon balance, but it can also affect soil biogeochemical cycling through physical and biological feedback mechanisms. Recent studies indicate that […]