Differences in the rhizosphere effects among trees, shrubs and herbs in three subtropical plantations and their seasonal variations
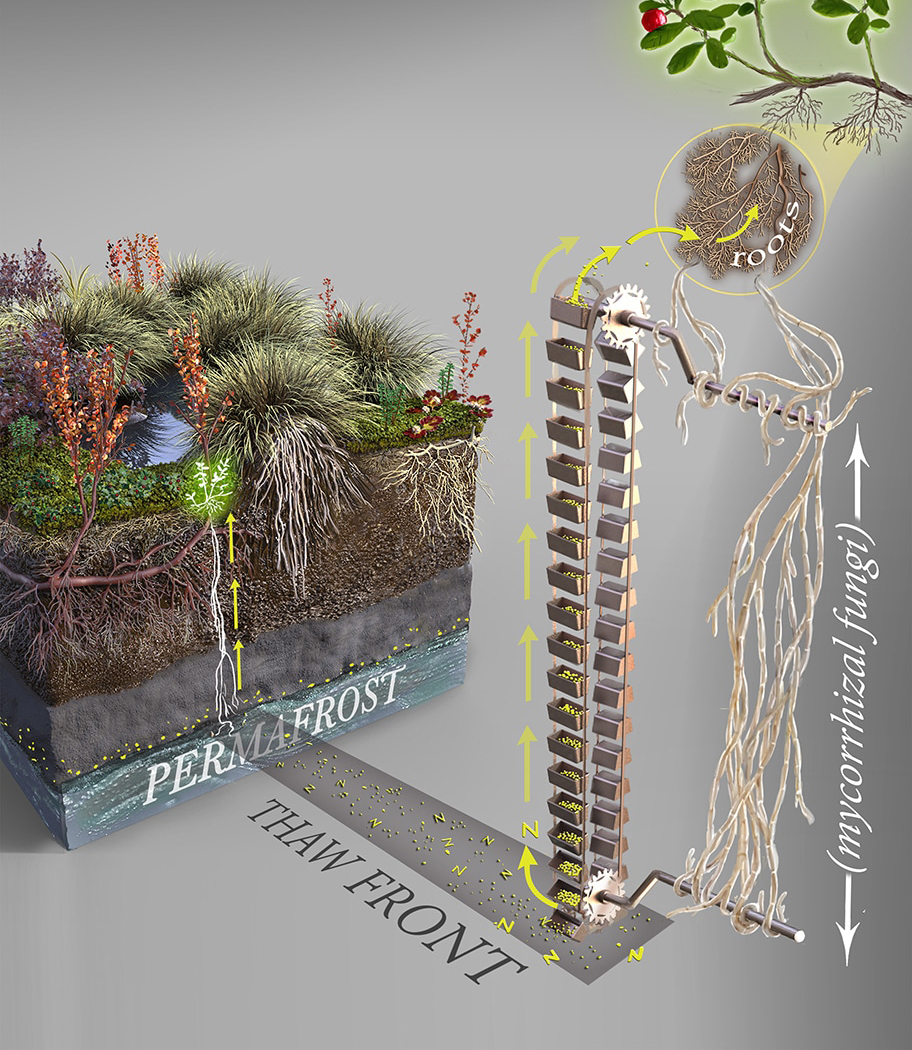
Unique soil properties in rhizosphere can affect plant growth and biogeochemical cycles of ecosystems. While rhizosphere has been widely investigated, little is known about differences in the rhizosphere effect (RE) between co-existing overstory trees and understory shrubs and herbs in forest ecosystems. In this study, we investigated REs on soil […]