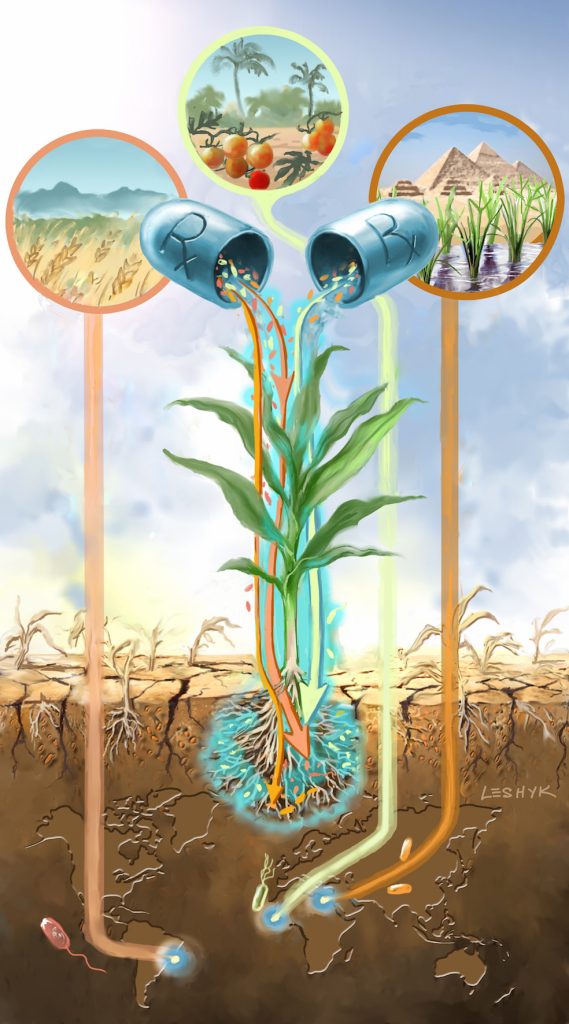
Could drought-quenching bacteria stabilize future crop yields?
ECOSS researchers recently published findings in the scientific journal Plant and Soil showing that rhizosphere bacteria could help reduce crop losses due to drought. See the full article Listen to an interview by Knau with Rachel Rubin Watch an interview with Rachel Rubin for Arizona PBS